Table Of Content

With ASD, there is a lack of social interaction, impairment in nonverbal behaviors, and a failure to develop normal peer relations. A child with an ASD tends to ignore facial expressions and may not look at others; other children may fail to respect interpersonal boundaries and come too close and stare fixedly at another person. ABA stands for applied behavior analysis and is considered the most effective treatment for autism by the medical, psychological, and behavioral health communities. Supported by decades of empirical research, coverage for ABA treatment is mandated in the United States, with treatment taking place in your child’s home, community, school—or in centers designed especially for ABA therapy and related services.
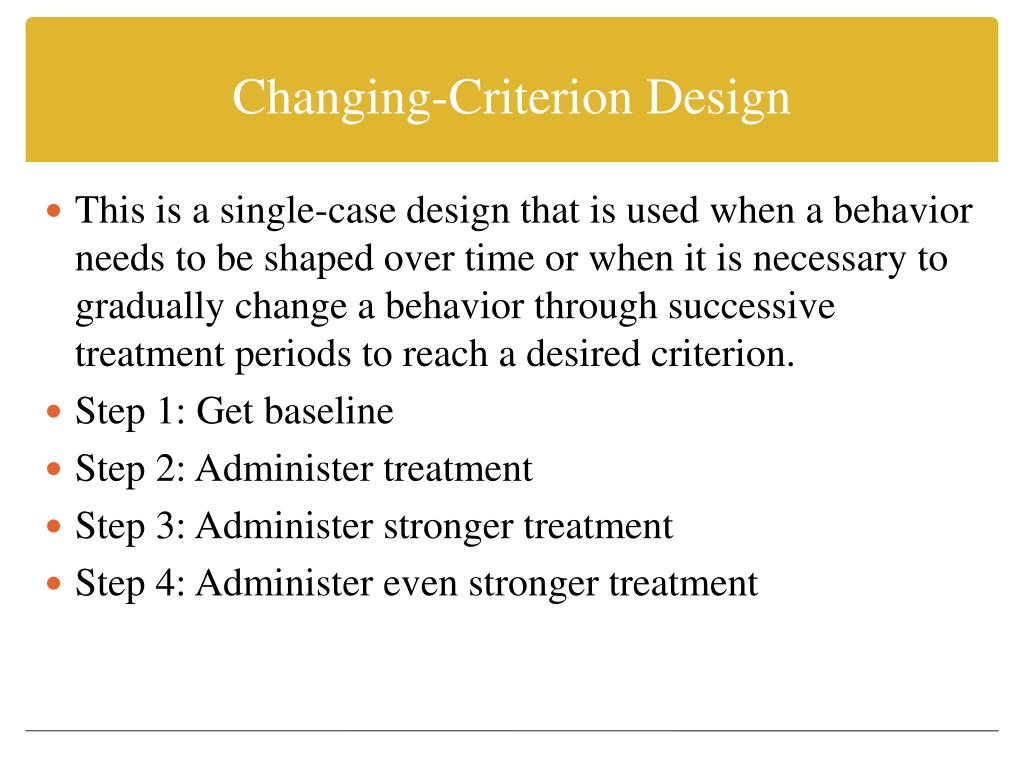
Parallel Treatments Design: A Nested Single Subject Design for Comparing Instructional Procedures.
Certification programs for practicing ABA therapy are provided by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB). Board-Certified Behavior Analysts with a master’s degree and appropriate training are identified by the initials BCBA after their name; those with a doctorate-level degree are identified by the initials BCBA-D. (In Florida only, a BCBA may use the initials FL-CBA or the term Florida Certified Behavior Analyst). The length of time spent in ABA depends on the severity of the problem and individual rate of improvement. ABA can also help aging adults cope with the losses that come with age, like memory, strength, and relationships. For young and old, ABA can help individuals manage some of the lifestyle challenges that accompany many mental and physical health conditions.
How does ABA therapy work?
These individuals were required to throw three darts and hit the board each time in order to progress to a further distance or height closer to the standard 5 ft, 8 in. Thus, the behavioral performance of throwing three darts with 100 % accuracy was stable and the task topography of distance and height changed. The second variation, the distributed criterion design (DCD), is proposed to manipulate one behavior across interdependent but discrete contexts or interdependent behaviors in one context (McDougall 2006). Gradual criterion shifts are not required in this variation as it is not a design targeting increasing or decreasing a dimension of behavior, but rather it functions as a behavior or response management system (e.g., self-management or self-monitoring). This management system has been demonstrated by McDougall using an overarching fixed dependent variable; however, the design could be implemented with a non-fixed variable as well. Although the sequential changing of multiple behaviors is often desirable (especially in echobehavioral interventions), and it is correct that manipulating rates of one behavior will necessarily impact other functionally similar behaviors (Delprato 2002), the value of this design is questionable.
Planning and Ongoing Assessment
The remaining 106 articles yielded a total of 267 CCD graphs (236) or intervention data (31). Articles were located in 57 different journals; see Table 2 for a summary list of journals. From these journals, 11 articles were published between 1971 and 1979 (10.4 %), 24 articles between 1980 and 1989 (22.6 %), 18 articles between 1990 and 1999 (17.0 %), 35 articles between 2000 and 2010 (33.0 %), and 18 articles between 2011 and 2013 (17.0 %). The exact causes of autism are unknown, although genetic factors are strongly implicated.
After pulling references from the first five (Brunner & Seung, 2009; Dawson & Bernier, 2013; Makrygianni et al., 2018; Rodgers et al., 2020; Shabani & Lam, 2013), it was found that the references in the remaining five reviews were duplicates of previously identified references. Records from Brunner and Seung (2009) that were categorized into treatment models that did not fulfill the definition of ABA as per the current review were not considered. In addition, the secondary review by Vismara and Rogers (2010) was not considered because it was a narrative review. After removing duplicates or entries already existing in the database search, 1,577 entries remained from the database search and 525 from reviews, for a total of 2,102 records.
Decreasing classroom misbehavior through the use of DRL schedules of reinforcement.
Records recording improvement in adaptive behavior and emotional outcomes had follow-up measures 67% and 64% of the time, respectively. Studies reporting improvement in autism symptoms had follow-up measures 100% of the time (see Appendix 5, Table S7). Within the current cohort, out of the study records that signified some improvement, the frequency of mastery/criterion measures varied. Measures of mastery/criterion ranged from 0% and 14%, respectively, for autism symptoms and problem behavior improved outcomes, to 25% and 29%, respectively, for adaptive behavior and social/communication, and 43%–49% for cognitive, language, and emotional improved outcomes (Table S7). With regard to generalization, no study records showing improvements in autism symptoms assessed any measure of generalization.
ABA therapy programs can help:
Clinical guidelines approved by the Medical Policy & Technology Assessment Committee are available for general adoption by plans or lines of business for consistent review of the medical necessity of services related to the clinical guideline when the plan performs utilization review for the subject. Due to variances in utilization patterns, each plan may choose whether to adopt a particular Clinical UM Guideline. To determine if review is required for this Clinical UM Guideline, please contact the customer service number on the member's card. Marked deficits in verbal and nonverbal communication skills; social impairments apparent even with supports in place; limited initiation of social interactions; and reduced or abnormal responses from others. For example, a person who speaks simple sentences, whose interaction is limited to narrow special interests, and who has markedly odd nonverbal communication.

The majority of study records reported improvement across all outcome categories, with 63%–88% of study records reporting improvement across the various outcome measures. In contrast, 0%–2% reported regression, 13%–36% reported mixed results, and 0%–13% reported no change (Fig. (Fig.22). Inclusion criteria for article selection during the initial search comprised (1) English language articles that are (2) about the effects of ABA on (3) children and youth (birth to 18 years) with NDD/D, within (4) the timeframe of January 1, 1997 through December 31, 2020. As described above, screened articles included from selected reviews and secondary reviews were exempt from the date range limitations. A small portion of the 267 studies conducted intervention training with participants prior to implementation (18.7 %). Functional behavior assessments (8.6 %) and preference assessments (12.4 %) were not frequently reported.
Data Coding and Synthesis
At LEARN, we refer to our approach as contemporary ABA to distinguish our therapy from the older, more structured form of treatment. The IRCA Reporter is filled with useful information for individuals, families and professionals. ABA is considered an evidence-based best practice treatment by the US Surgeon General and by the American Psychological Association.
One such method of naturalistic teaching is through the focused intervention practice of PRT, developed by Koegel and Koegel (2006), which is focused on improving the self-initiative and motivation of a child to communicate effectively in common real-life settings (Mohammadzaheri et al., 2015). Another focused intervention practice and naturalistic teaching method is FCT, a differential reinforcement-based procedure developed by Carr and Durand (1985) that reduces problem behaviors by replacing them with more appropriate communicative responses. Results indicate that the CCD has been utilized with varied populations, in varied settings, and targeted a wide variety of behaviors; however, the majority of CCD studies were structured in ways which threatened experimental control. Approximately 25 % (i.e., 26 studies yielded 69 graphs) of data reviewed met all requirements necessary for adequate control (see Table 1). This suggests some fundamental lack of understanding of the science underlying the CCD. Specifically, most studies lacked variation in phase magnitude (and did not compensate with a reversal), lacked variation in phase length, or implemented two or fewer changes in criterion; while some restricted responding so that criterions were forcibly met and or could not exceed the criterion.
There are some exceptions to this, where in some circumstances a child may exhibit normal development for approximately 2 years followed by a marked regression in multiple areas of function. A total of 1,337 records were removed during title, abstract, and full-text screening because they met the exclusion criteria, were duplicate records, were reviews, or contained only non-ASD diagnoses. Multipart studies were separated into discrete records, yielding a total of 849 study records.
The multiple baseline design is a poor model for the DCD in that it is significantly weakened by interdependence of baselines or results, whereas interdependence is an established expectation of the DCD. It is a fundamentally weak design that adds little to the literature in its present form. According to the BACB’s 2014 guideline, comprehensive ABT should include one-on-one treatment with a certified or licensed physician, qualified healthcare provider, or ABT technician of between 30 to 40 hours per week. This analysis, however, did not determine the optimal number of treatment hours per week. Because family members know that early intervention helps children on the autism spectrum learn new skills and decrease problem behaviors, they often want to consider behavioral therapies for their child.
Approximately 63.7 % of studies conducted did not implement either a mini or full reversal. Again, a reversal, mini or full, is not a required design component of the CCD; however, implementation of either type of reversal considerably increases design strength by demonstrating the independent variable can increase or decrease responding accordingly. The majority of the studies did not use the CCD as a shaping procedure and therefore the dimension of the behavior being modified, in most cases, was in the individual’s repertoire and should be compliant to directional shift. Therefore, specific target behaviors were recorded and classified following data collection for summation purposes. Participant age was classified as child (1 to 18 years) or adult (19 and above). Visual Communication Analysis (VCA), which can be considered an extension or augmentation of ABA, is a personalized treatment for individuals with ASD.
Within the cognitive, language, and social/communication outcomes, 37%–40% of comparison records found that one method exhibited greater improvement than the other, whereas 47%–56% had mixed outcomes. This is similar for adaptive behavior, where 52% found that one method exhibited greater improvement and 39% were mixed. On the other hand, outcome measures for problem behavior and autism symptoms more clearly showed that one method exhibited greater improvement, at 65% and 70% (7 out of 10 records), respectively. In 2023, Eckes and colleagues published a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing comprehensive ABA-based interventions to a control intervention and with at least 5 participants per group. Studies varied in intervention intensity and duration, control intervention and outcome measures. In a meta-analysis of post-treatment improvement measures, the investigators found a statistically significant improvement after ABA-based treatment compared to control interventions (9 studies, SMD [standardized mean difference], 0.37, 95% CI, 0.03 to 0.70).
Choose one committed to clinical excellence and active in ABA-related conferences and trainings. Given the evolving nature of science, it’s important to find a partner who stays updated on and engaged with the research. ABA has evolved significantly since that time period, with research advancing therapeutic interventions and protocols—and transforming the overly rigid, structured approach from the early years into something far more child-centered and age-appropriate.
For example, in teaching social skills, a learner might be shown a video of a person saying thank you when given a toy or other object, and then asked to repeat the behavior as the teacher hands them an object. As previously reported, 25 interventions used a stable criterion of performance and therefore had a total of one criterion. As mentioned, it has been suggested that a changing criterion have at least two criterion shifts or two subphases of “B” within a study (Kazdin 2011, p. 172). Just over half of the studies varied phase length between criterions at least once (55.8 %) and a considerable proportion varied length two or more times (35.6 %).

No comments:
Post a Comment